REEMS
Range Extension Engine Management System (REEMS)
Background
The REEMS project aim is to improve the mechanical performance models used to establish a range-extension methodology and to introduce the use of computational intelligence (CI) techniques to operate a real-time range extension engine management system. This project is funded by the East Midlands European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) via the Transport iNET.
The proposed system will include a journey planner, with real-time trip analysis that will take account of road and environmental conditions for the whole journey and a driver profile. The performance model will be based on real-time analysis of the vehicle operation, and will be tuned to each vehicle. The CI system will optimise the operation of the REEMS taking into account of the complete trip requirements, not just the instantaneous data
REEMS Architecture
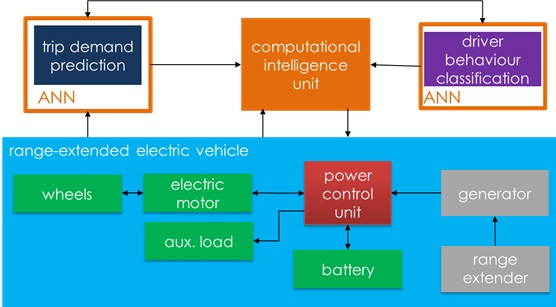
The key output will be a range extender strategy to manage power distribution by controlling the current power delivery based upon real-time conditions and predicted near-time load changes. REEMS will use vehicle instantaneous demand, along with state of charge (SOC) as an input into the CI unit that will optimize the power flow while considering the predicted journey-related power requirements, adjusted to the current driver behaviour, against available stored energy.
The CI unit is based on the fuzzy logic concept whereas the prediction of journey power requirements and driving style recognition were developed with use of artificial neural networks (ANN). The vehicle will be instrumented to obtain the required input parameters, to be fed in real time into the ANN.
Contact
For further information please contact Daniel Paluszczyszyn (paluszcol@dmu.ac.uk)